One of the most crucial stages while designing a new product is the prototyping stage. This is where the magic happens. Prototypes take an abstract idea to a reality stage, hence making it tangible and testable.
They can be used for a great number of iterations, user-testing, and functionality testing before final decisions on large-scale production. However, such a critical stage can be costly; having an idea of some of the factors that add to prototyping expenses is very important in effective budgeting.
This blog discusses the cost of prototyping for product design services and some recommendations firms should make to budget for this process.
 Table of contents
Table of contents
- What's prototyping and why is it necessary?
- Cost of prototyping
- Estimating prototyping costs
- Prototyping budgeting in your company
- Wrap up
- How Cad Crowd can help
What’s prototyping and why is it necessary?
Prototyping refers to an early version or model of a product developed in order to give an image and test the design, functionality, and usability of the product. It is thought to be a proof of concept to help point out flaws in the design, improve its features, and fine-tune the overall user experience any final products are put into the market. There are various types of prototypes, such as functional prototype, among others depending on purpose.
- Near-production prototype: Almost fully developed prototype, which has been subjected to final testing and marketing.
- Proof-of-Concept (PoC): To test a simple idea or concept
- Visual prototype: Focuses on the looks, and the product’s functionality isn’t that crucial
Prototyping is essential for several reasons: - It avoids expensive manufacturing mistakes
- Quality of your product would improve as it can be iterated on multiple times
- It will attract investors, and fund raising since it will give an actual version of your idea.
- It enhances the speed of decision making as it gives insight in user experience and also market viability.
RELATED: What are the main prototypes used by companies in industrial design prototyping?
Cost of prototyping
The cost of prototyping ranges from a few hundred dollars to several thousands, and this depends on various factors, such as the level of complexity in design, the material used, the kind of prototype in question, and the method or manner of prototyping. Here is an outline of some of the main factors determining the cost of prototyping.
Design complexity
The complexity of your product design is one factor in costing your prototyping. A simple design with less part content, or whose shape can be easily replicated may be more readily prototyped and cheaper, but designs with a lot of mechanical or electrical complexity can run much more expensive. Again, the more detail in your design, the more time and work will go into creating a usable model, making cost go up.
For instance, a simple consumer product, such as a plastic container, will most likely just require fundamental 3D printing, probably inexpensive. On the other hand, a high-tech consumer product with embedded electronics or sensors or special materials will probably use advanced prototyping techniques most likely to be costly.
Materials
The type of material being used in the prototyping greatly determines the final cost. Prototypes can be made from any type of material, including plastics, metals, and composites, and the pricing and processing are also different for various materials. Aerospace-grade alloys or specially constructed polymers really drive the cost up drastically from standard plastics or 3D printing material.
- CNC machining: High in precision, very well suited to the metal prototypes, though equipment and material costs will be steep in this type of prototype.
- Handcrafting: Handcrafting with inexpensive material is used for simple models.
- Injection moulding: It can be applied for rugged prototypes. But it is expensive due to the development of moulds.
Prototyping technique
There are several ways a prototype can be prepared, each with related costs. Among some common techniques used include:
- 3D printing (additive manufacturing): 3D printing is the most widely used technology in rapid prototyping. The payoff in using 3D printing is that it rapidly converts digital models into physical products through a wide array of materials, sometimes very quickly with short production time and flexible design but soon becomes expensive in material and machine time.
- Casting: Casting is used for a wide range of products. It is much more manual intensive than injection molding. Cost in casting depends upon the material and the complexity of the material.
- CNC machining: Cutting, drilling, or milling of plastic, metal, or composites into a desired shape. This is a precise process to detail and has a cost to it, meaning it’s rather pricey. Thus, it’s more applicable for functional prototypes.
- Injection moulding: Injection moulding is a very fast and cost-effective method of producing significant quantities of proto-typed items, especially for articles that require strength. However, the cost incurred when making design and building tooling is very great at the very beginning.
RELATED: 10 tips on how to find the best prototype engineering firm services
Outsourcing vs. in-house prototyping services
Finally, the greatest decision concerning prototyping has to do with whether the task should be outsourced to a professional service or done in-house. Each has its pros and cons.
- In-house prototyping: Companies with appropriate and readily available equipment, such as 3D printers or CNC machines, etc. usually resort to in-house prototyping due to cost-cutting reasons. It is suitable for simpler prototypes or circumstances wherein the rate of iteration is high. It, however, requires significant investment in machinery, expertise, and maintenance, thus proved to be quite cost-effective for large companies or frequent prototyping requirements.
- Professional service contracting: Many product design houses are professional services firms specializing in prototyping. They can provide full service: from design consultancy, material selectivity, and production of the prototype. The tools, expertise, and resources it has are all among those that can lead to quality prototypes. It is very costly, around $1,000 to $20,000, depending on the level of complexity.
Prototype iteration and testing
Most products require many iterations to the final. Each iteration provides a chance to test the design, even up to the response from the users, as well as to make necessary adjustments or for some r`esults in the performance. This is costly because every version will be demanding new materials, labor, and other resources.
Testing is another prototyping activity. Testing may include performance in physical settings, usability by the users, or compatibility tests with other systems. The more intense testing will be the more expensive prototyping phase is going to be.
Timeline
The cost may also depend on how soon you need the prototype done. When there is a time constraint, sometimes it means hastening up the process, and this would cost more based on rushed shipping and more man-hours or faster production methods.
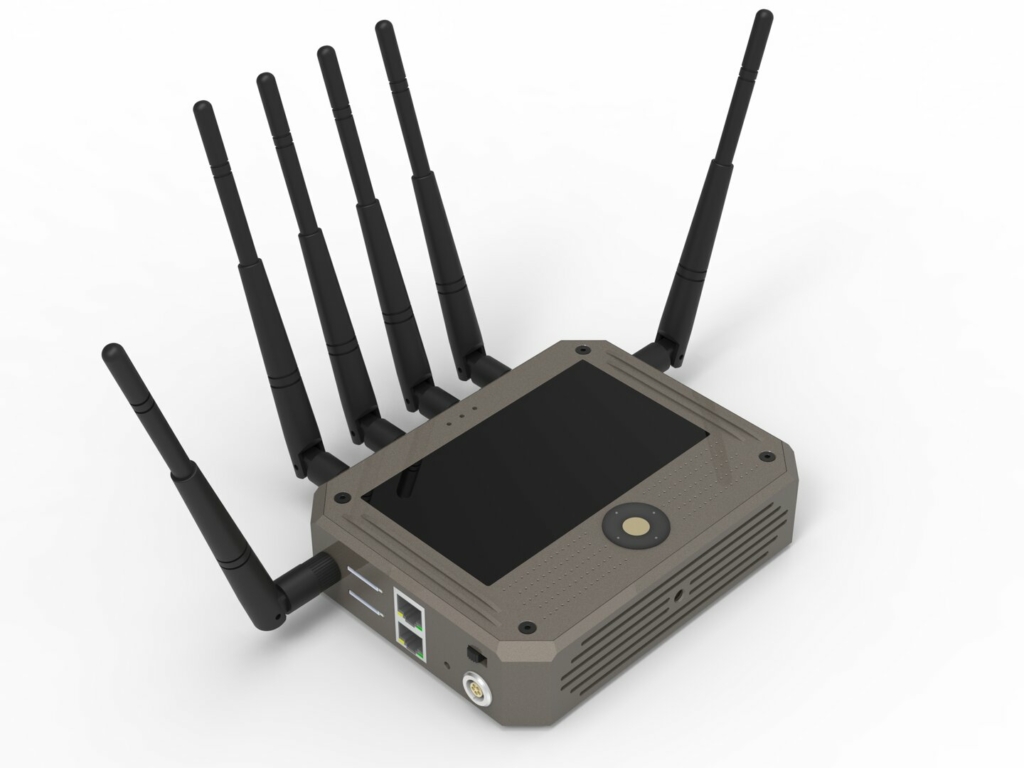

Estimating prototyping costs
It is great to estimate prototyping costs early in the development process so that budgets could align with needs. Normally, prototyping cost would be broken down as follows:
- Low-cost prototypes: The estimated range is from $100 up to $2,000, which depends on its simplicity, like 3D-printed prototypes or a basic functional model, depending on the materials and production method used.
- Mid-level prototypes: With CNC machining, in metal parts or with small runs of injection-molded products, the costs will run from $2,000 to $10,000.
- High-end prototypes: More detailed or even complex prototypes with sophisticated materials or electronic components may reach between $10,000 and $50,000 or more for multiple iterations.
These costs differ based on the factors enumerated above, so it is essential to collaborate closely with your product development team to create a detailed budget.
Prototyping budgeting in your company
To budget effectively for prototyping, consider the following steps:
- Define goals and requirements: State exactly which kind of prototype is needed (proof of concept, functional, visual, or near-preproduction). Determine the level of detail, materials, or functionality that needs to be tested.
- Choose the right prototyping method: Depending on your goals, choose the right prototyping method. Quick iterations can be ideal with 3D printing, while CNC machining or injection molding can be good options for functional or production-ready prototypes.
- Iteration: Several prototypes can be expected, especially in the refinement phase. Since iteration impacts time and resources, keep these costs in your mind while planning your budget.
- Collaboration with a design consultant: If after reading you are still unsure how to factor in the cost breakdown into your budget, then collaboration with a design consultant can further help break it down and clarify the options. Many product design services can offer affordable prototyping solutions based on individual needs.
- Contingency fund: Always put aside some amount of your budget for unintended costs. Prototyping can be unpredictable sometimes, and having a contingency fund will always get you through those unknown costs.
- Set for long-term savings: Though an initial investment, prototyping will save one money in the long run as it limits production mistakes and maximizes the final product’s market success.
Wrap up
Prototyping is another development stage where huge involvement with costs and resources is incurred. Knowing what affects prototyping costs as well as how to plan a budget can help businesses prepare for this very important phase of their product design process.
How Cad Crowd can help
Regardless of whether you are manufacturing something that falls in the category of simple or is more complex, an investment in a proper prototype will mean better outcomes in terms of quality, product, and standing in the market. Cad Crowd will ensure you are at the top of the game. Request a quote today.

