Computer-aided engineering (CAE) had limited applications in the past. It was mainly used for research and development projects of advanced designs or technologies by large corporations or big-budget government projects. The proliferation of computer-aided design (CAD) has brought broader recognition and implementation of CAE in the manufacturing industry.
Product designers and engineers routinely use the tool to help accelerate product development. CAE software has reached a point where it can tackle highly sophisticated designs, allowing manufacturers to introduce their products to the market in record time.
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
RELATED: How Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Services are Used by Engineering Firms
CAE simulations
Among the most significant advantages of computer-aided engineering (CAE) is the capability to simulate product performance and usage in the virtual world. By simulating multiple real-world scenarios on screen, engineers can see and predict how a particular product should perform, behave, and react when exposed to various environments and situations.
A prime example is how carmakers no longer use an actual vehicle to do a crash test to see what damage the impact would inflict. A virtual crash test using CAE software helps engineers recognize the weak points in the design and subsequently improve them to make the car safer.
In the past, it took two to three sacrificial cars for the crash test. The simulation program can reduce design costs by anticipating and preventing failed tests. Simulation results tell the engineers which parts to improve before finalizing the design. Ultimately, the factory only has to send one vehicle to perform the test and pass it with flying colors.
RELATED: What are CAE Engineering Costs, Company Consulting Rates & Services Pricing?
Another typical example is how engineers optimize cost-efficiency by subtracting materials from a design. Once again, simulation results can reveal how extensive the subtraction should be to allow for a minimum footprint (and manufacturing cost) without sacrificing structural strength or performance. The same thing applies to product ergonomics, fuel consumption, and durability. In general, it is difficult to exaggerate the role of CAE in modern design and manufacturing industries.
Real-world tests with a physical prototype used to be the foundation of robust product research and development, and now CAE simulations are used. CAE has not eliminated the need for physical testing, but it does improve the efficiency of such testing to a considerable degree. The software makes it possible to build both a virtual prototype and a digital environment where it can be tested without involving potentially expensive mock-ups.
Many startups and new entrepreneurs still rely on physical prototyping, despite knowing that CAE offers a more practical solution. The biggest hurdle that prevents the broader adoption of CAE is cost. Some commercial CAE software packages are subscription-based, while others are one-time purchases. The subscription fee varies from $30 to $100+, and premium CAE can cost tens of thousands per user. The steep learning curve is another concern. Even though there are helpful resources online, it still takes months, if not years, for an average person to learn all the basics.
RELATED: The career path of CAD engineering, salary, rates, and more
Who uses CAE software?
Every company that designs and sells mass-produced goods should use CAE to improve business efficiency. The improvement can be from a lower manufacturing cost, a shorter design cycle, and a quicker time-to-market phase. Currently, the primary users of CAE are:
- Automotive companies: whether the company makes cars, motorcycles, trains, or aircraft, CAE software offers more than enough tools to simulate vehicle performance in the real world.
- Structural engineering companies: architectural firms can use simulation services or programs to experiment with multiple design options before construction begins. Unlike CAD, which puts a heavier focus on the modeling side of a project, CAE delivers both accurate virtual modeling and its engineering calculations. The firms can also perform impact and stress analyses on screen.
- Industrial equipment companies: physical testing for large heavy-duty industrial machinery is resource-demanding. CAE helps optimize engineering design services from the early development phase to completion. Virtual test for strength, reliability, safety, and endurance significantly reduces design cost.
A product development process requires several prototype iterations. Since each iteration represents a progress milestone, every design change requires a new mock-up. Cost efficiency hinges upon having every iteration built right on the first attempt. If the product features unique parts or custom components that need specialized tooling, a single prototype can cost hundreds, if not thousands, to build. Performance and endurance tests can also damage the physical prototype beyond repair, which means engineers must make a replacement.
RELATED: CAD vs. CAE: What Stage of Product Development is Your Business In
Standard CAE software features
Engineers can build an analytical product design model thanks to CAE-based virtual prototyping. A digital mock-up in CAE is more than a wireframe visualization but a technical representation of the physical object. For example, the software allows engineers to input information about a model’s materials and physical properties.
A virtual prototype represents the product’s structural rigidity and overall strength. The PCB layout and internal components are based on real-world technical specifications for an electronic product.
A virtual prototype built accurately to the product specifications should generate reliable simulation data for further analysis. Some of the most common virtual simulations include:
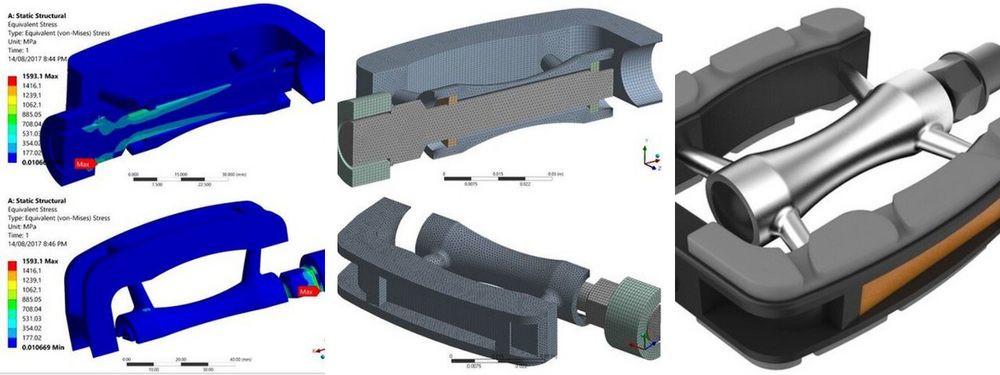
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA): FEA is a numerical method that breaks down an engineering problem into more minor specific questions, known as finite elements. In other words, FEA untangles a complex challenge and presents it as multiple yet more manageable questions. The results give an overview of how an object, material, or shape behaves when affected by external forces.
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): if FEA deals with solids (objects with definite shapes and volumes), Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) models the behavior of fluids and gases. It gives clear insight into how they interact inside an enclosed chamber or react when exposed to surfaces of different materials.
- Mechanical Event Simulation: Mechanical event simulation aims to see how objects react to a real-world situation. Product waterproofing or durability test falls into the category. For example, engineers can see how long until a smartphone shows signs of damage when submerged at a certain depth. The simulation software indicates the durability factor of each hardware component and suggests design changes to improve strength and protection. The same principle applies to a drop test.
- Thermal Simulation: a virtual test to determine how an object reacts to changes in temperature. In a product that generates heat during operation, engineers need to know how to design a proper cooling mechanism across the enclosure to prevent malfunction due to overheating issues. It is a test for every product that relies on thermal management to function well, such as car engines and pressure vessels.
- Electronic Simulation: most often used for electronic products, the simulation tells engineers whether the components are affected by electromagnetic interference.
In the construction industry, CAE software plays its role in structural analysis. A simulation helps determine the effects of both dynamic and static loads on building components and assemblies. CAE gives a vivid picture of how the components react under stress and vibrations. Ideally, building architects and engineers utilize simulation early in the design process to identify flaws and reduce costs throughout the project.
RELATED: What are CAM Engineering Costs, Company Fees, & Consulting Service Rates?

Why use CAE design services
Extensive virtual prototyping and simulation cost money, but it will only be a fraction compared to the budget required for physical mock-ups and real-world analysis. As CAE becomes more advanced, it is possible to configure multiple otherwise too-expensive scenarios to replicate in physical testing. Recreating any specific environment and usage condition for product testing has become practical, and engineers can change every imaginable variable in a breeze to ensure the accuracy of analysis results.
Incorporating CAE design services is, therefore, beneficial to almost every aspect of product innovation:
- Cost efficient: thanks to CAE’s virtual nature, the product development process doesn’t have to undergo multiple product prototyping stages. Many prototypes are still built, but every single one is a digital mock-up. A company can create a dozen iterations of the same product using only a computer. For example, engineers who build camera drones can simulate how the vehicle performs under various weather conditions. Engineers can make changes without creating a drone, regardless of the test results.
- Short design cycle: changes in design and the subsequent simulations to test performance are no longer time-consuming and resource-demanding. Since all the prototypes (except the final prototype) are built on screen, the overall design cycle is shortened. Engineers are spoiled with the opportunity to improve product usability and functionality well before the manufacturing phase. The simulation also does not require additional resources.
- Test accuracy: hundreds of different variables can be involved in real-world testing. CAE software can simulate every thinkable complex scenario. Major and minor details are configurable, from product materials to ambient temperature, assembly design, and weather conditions. As the number of variables increases, the test accuracy better represents real-world results.
Computer-aided engineering (CAE engineering) is prototyping and engineering work done on a screen based on real-world variables. Simulation represents physical tests to demonstrate how a product performs under various conditions. As long as the engineering data and environmental variables are accurate, the simulation should generate identical results to physical testing results.
RELATED: How Much Do Engineering Design Services Cost for Company Design R&D?
How Cad Crowd can assist
Cad Crowd is your one-stop solution for bringing your product innovation ideas to life. Our expert community of engineers and designers specializes in Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) and Design Services, empowering you to optimize your product’s performance, reduce development costs, and accelerate time-to-market.
Ready to unleash your product’s full potential? Get started with Cad Crowd today and revolutionize how you design and engineer your products. Request a free quote to take the first step toward your product innovation journey.
